Table of Contents
Entendendo a Política de Seguraça de Certificados
O que são os certificados exigidos pelos browsers?
Eles garantem a identidade e procedência de um site, sendo utilizados na segurança de dados, de modo que os mesmos não fiquem expostos enquanto navegam na Internet.
Por isso a importância de que sejam certificados e validados por alguma entidade certificadora.
Agora, se o certificado é inválido mas você conhece o site que vai acessar e confia nele, então a navegação embora seja considerada insegura pelo browser, continuará mantendo o sigilo dos dados enquanto trafegam pela Internet.
É justamente isso que justifica utilizar o protocolo “https” que você vê nas URLs de sites seguros — manter os dados indisponíveis enquanto navegam pela rede.
No protocolo http (não seguro), os dados são transmitidos na forma original com que são enviados e portanto, qualquer aplicativo de sniffer pode interceptar os mesmos e serem lidos diretamente, sem qualquer dificuldade.
Os sniffers assumem diversas formas. Há sniffers de pacotes, Wi-Fi, redes e IP, entre outros. Mas todos têm uma coisa em comum: um sniffer é um tipo de software que captura todo o tráfego que entra e sai de um computador conectado a uma rede.
Mais informação, vide:
Certificado Digital: O que é?
Browsers Com Política de Segurança Estrita

Alguns sites utilizam certificados autoassinados, sem validação por uma entidade certificadora, face aos objetivos de utilização que dispensam tal requisito.
Alguns browsers (navegadores) rejeitam acessar sites cujos certificados são autoassinados porque adotam políticas de segurança estritas.
- Google Chrome
- Opera
Outros browsers, contudo, adotam uma política mais flexível, advertindo o usuário de que o site não é confiável, uma vez que o seu certificado foi emitido por si mesmo, e não por uma autoridade certificadora de identidade e origem que mereça fé pública.
Você precisará desses browsers quando precisar acessar um site que você conhece e confia embora o certificado seja autoassinado.
Browsers Com Política de Segurança Flexíveis
- Safari (Windows 10/Windows 7)
- Internet Explorer
- Firefox (Mozilla)
Abaixo, fornecemos os detalhes de configuração por browser.
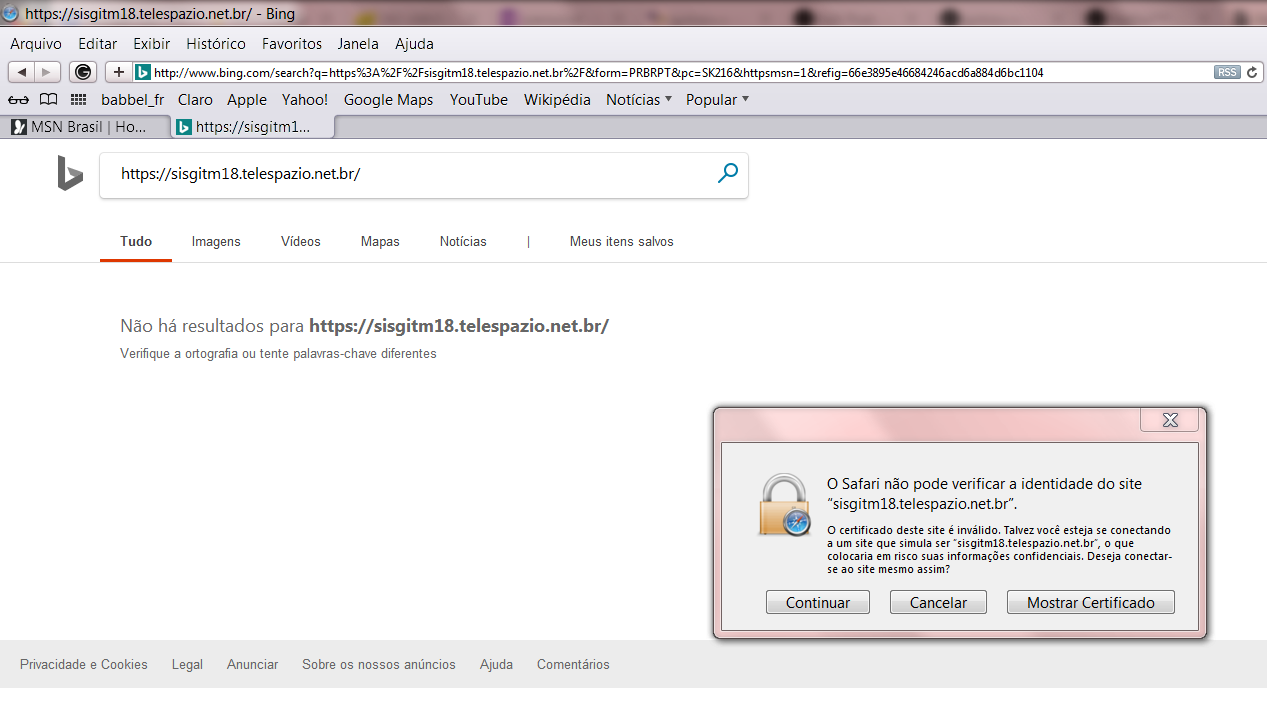
SAFARI – VERSÃO PARA WINDOWS
É a versão mais condescendente com certificados autoassinados.
Testado no Windows 10, o acesso foi direto, sem qualquer aviso.
No Windows 7, apenas um aviso, onde basta pressionar o botão “Continuar” para obter o acesso.
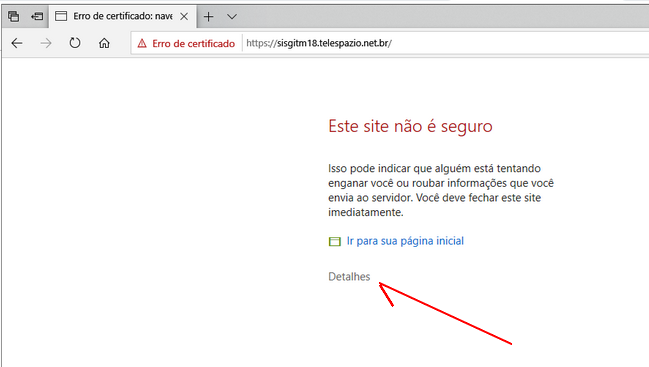
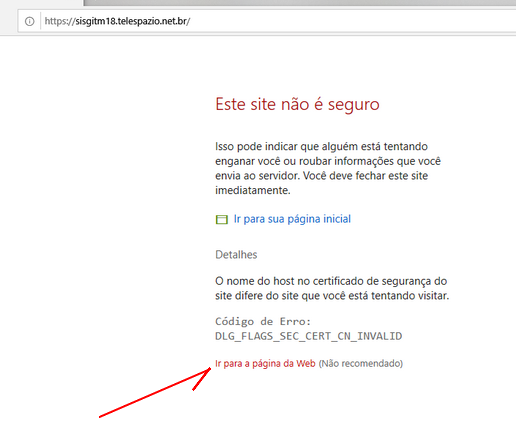
INTERNET EXPLORER
Browser padrão do Windows, adota uma política intermediária, advertindo o usuário e requisitando uma adição de exceção ostensiva.
Os detalhes deste procedimento estão descritos através das imagens abaixo.
Brazilian system analyst graduated by UNESA (University Estácio de Sá – Rio de Janeiro). Geek by heart.